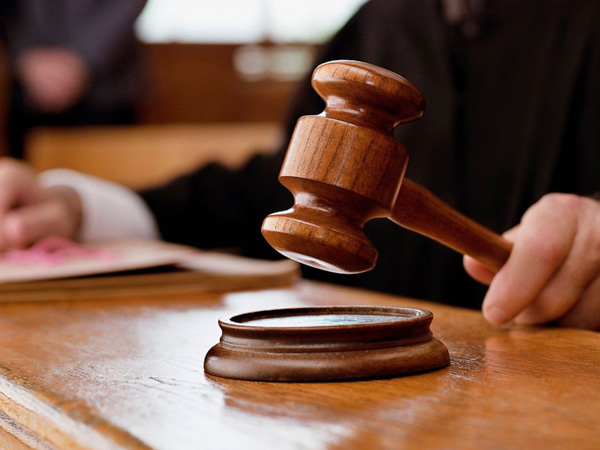
New Delhi [India], January 23 (ANI): Delhi High Court has recently discharged a government school principal from a case of death of a student due to negligence in a school in the Kapashera area in 2016. A charge sheet without prosecution sanction was filed against the principal and cognizance was taken.
The relief has been granted by the court after noting that the sanction to prosecute her was obtained after cognizance of the charge sheet was taken by the court.
The High Court said that the subsequent sanction can’t cure the initial defect in taking cognizance.
Justice Neena Bansal Krishan discharged Rekha Kakkar of the allegations.
“It is settled law that the Sanction had to be obtained prior to taking cognizance. Subsequent sanctions would not cure the initial defect in cognizance. Consequently, the application for dropping of proceedings against the petitioner, is allowed and she is hereby, discharged with the liberty to the prosecution, to take appropriate action,” Justice Neena Bansal Krishna ordered on January 17.
A petition was filed on behalf of the Rekha Kakkar, against the Order of July 13, 2018, Metropolitan Magistrate, Dwarka court calling the same as bad in law.
The magistrate court had rejected the objection taken on behalf of the petitioner for the cognizance of the offence taken in FIR under Section 304A read with Section 34 of the Indian Penal Code, 1860 (IPC) registered at Police Station Kapashera.
Advocate Dhruv Gupta appeared for petitioner Rekha Kakkar and submitted that the order of cognizance is bad and any subsequent sanction would not cure the inherent defect in taking cognizance.
He further submitted that if any subsequent charge sheet is filed against the petitioner, it must also be accompanied by an application for condonation of delay.
An FIR under Section 304A (Death due to negligence) read with Section 34 of the IPC, was registered at Police Station Kapashera, against the petitioner, who is the MCD School Principal, JE Contractor and one school maid.
It was alleged that one child, aged four years, had died due to drowning in a septic tank on account of the negligence of the accused persons.
The charge sheet was filed in the court on July 5, 2016, and cognizance was taken. Thereafter, a notice under Section 251 of CrPC and under Section 304A of IPC was directed to be framed against all the four accused.
The petitioner took an objection that the cognizance itself was bad since no prior sanction had been obtained against the principal of the school and the JE.
The prosecution, thereafter, got the sanction against these two accused and submitted it in the Court. However, the learned counsel on behalf of the petitioner again questioned the cognizance being bad in law as the subsequent sanction could not have cured the initial defect of taking the cognizance.
It was submitted by the Additional Public Prosecutor (APP) that it is an admitted fact that the sanction had been obtained after the cognizance was taken.
The High Court said in the order that if the application for condonation of delay is filed, the same may be considered, in accordance with the law. However, for the other accused, the trial shall continue, in accordance with the law. (ANI)
Disclaimer: This story is auto-generated from a syndicated feed of ANI; only the image & headline may have been reworked by News Services Division of World News Network Inc Ltd and Palghar News and Pune News and World News
HINDI, MARATHI, GUJARATI, TAMIL, TELUGU, BENGALI, KANNADA, ORIYA, PUNJABI, URDU, MALAYALAM
For more details and packages